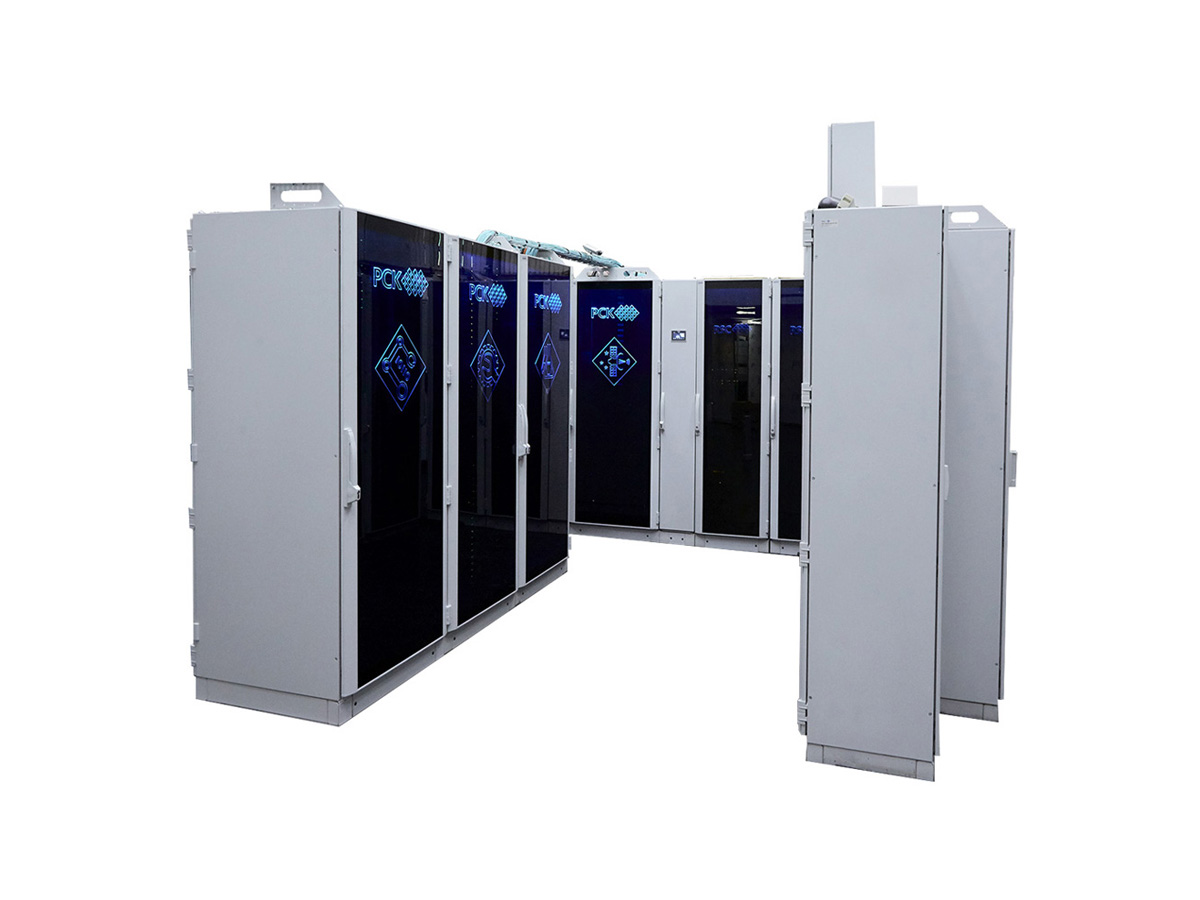
RSC BasIS Storage
- RSC BasIS Storage system is based on composable disaggregated architecture.
- Storage uses the NVMoF (NVMe over Fabric) protocol for accessing to NVMe drives via an RDMA network.
- Flexible dynamic storage configuration supports for the ZFS file system over NFS, the Lustre parallel file system and Intel DAOS cluster file system.
The storage system has been designed for record-breaking performance characteristics and enables dynamic management of disaggregated storage, combining all available resources into 'on-demand' clustered storage systems.
This approach enables the scalability of performance and storage capacity with deployment of new servers and disk devices providing protection of investments and lowered TCO.
Composable disaggregated infrastructure enables the most exact implementation of user requirements for each workload and creation of dynamically configurable multi-layered storage system.
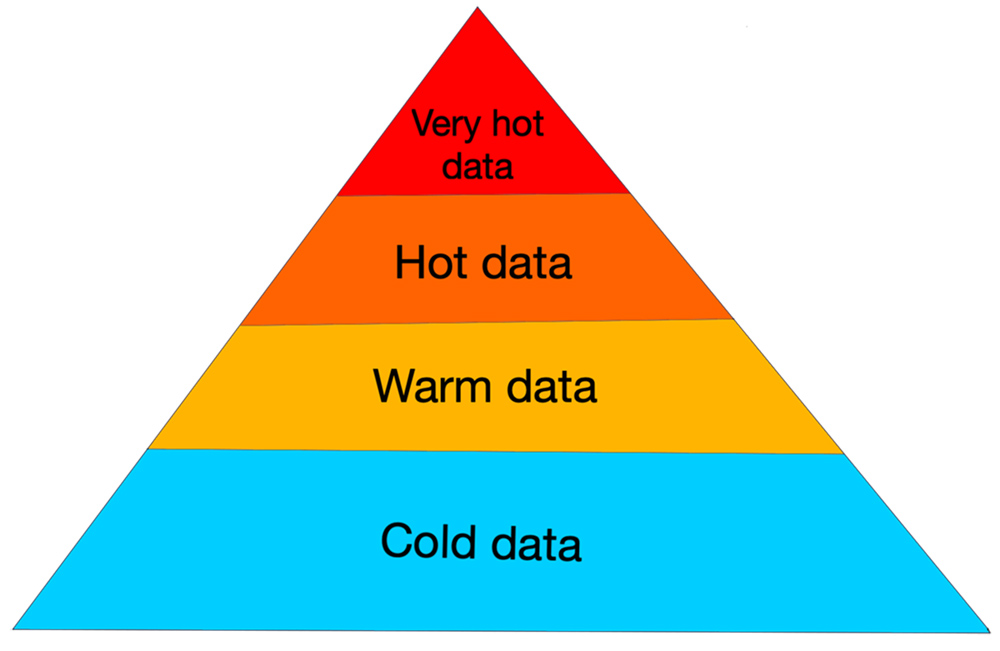
Structural principles
System based on NVMoF (NVMe over Fabric) protocol for accessing to NVMe drives over RDMA network, and RSC BasIS platform can dynamically select, combine and configure drives distributed in the computing framework based on the principles of composable disaggregated infrastructure, i.e. RSC's Composable On-Demand Storage software.
RSC’s main field of experience is creation of dynamic software-defined configuration scenarios focused on user data processing tasks. System configuration logic is not defined by administrator during installation, but can dynamically change during solution life cycle, enabling deep integration with specific user workloads.
The advantage of fully software-defined solution is that it doesn't have any restrictions of storage proportions as other computing systems.
This enables flexible software-defined storage on demand for multi-leveled systems with dynamic decisions on data layer performance and placement (e.g. using slower - “cold” or faster - “warm” and “hot“ data layers directly during processing.
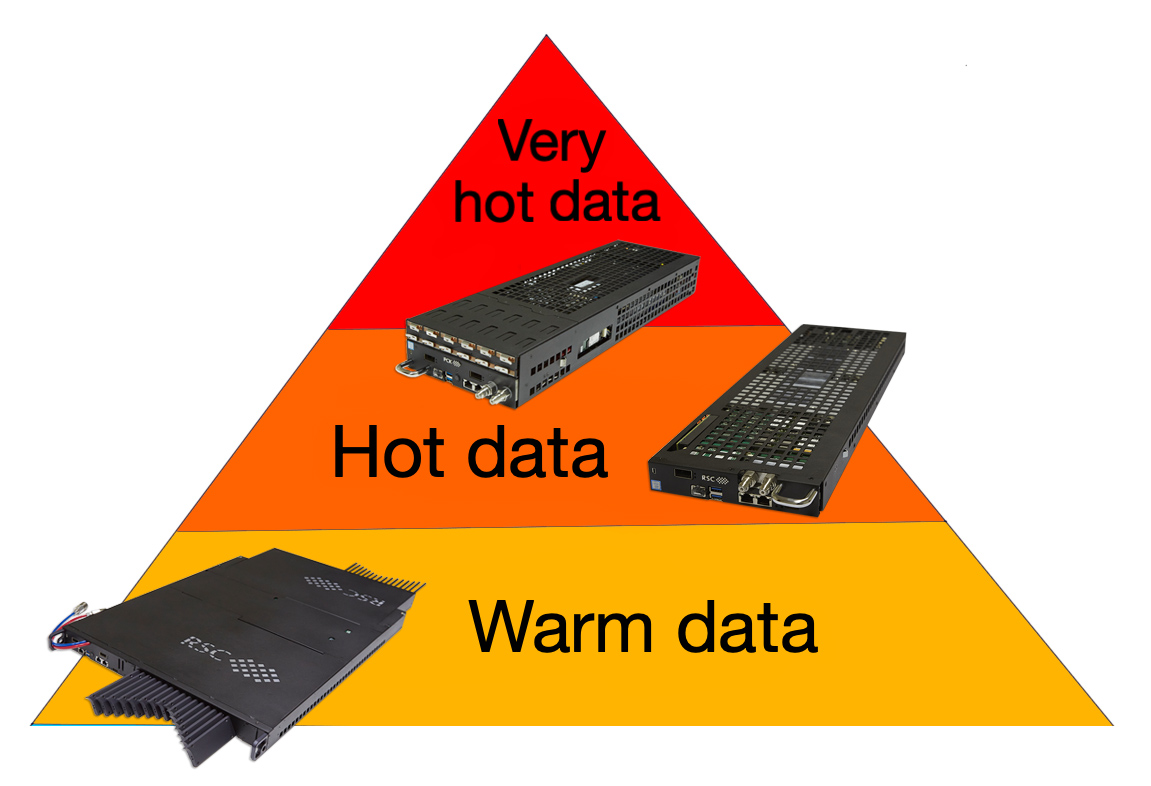
RSC’s hardware solutions
RSC can use various hardware to integrate composable storage systems, but the most efficient solution is RSC’s Tornado blade servers.
RSC Tornado TDN511S blade is created for “hot” and “very hot” data. It may include up to 12 NVMe M.2 drives and supports low-latency Intel® Optane™ SSD DC P4801X drives. Therefore, you can create a high-performance low latency 46 TB storage system in one node.
RSC Tornado TDN511, RSC Tornado TDN531, RSC Tornado TDN711 and RSC Tornado TDN811 work with “hot data”. They include from 2 to 4 NVMe M.2 or EDSFF E1.S SSD drives (high-performance low-latency Intel® Optane™ SSD DC P4800X drives supported). So you can create a high-performance low latency 15.68 TB storage system in one node.
RSC Tornado TDN551 AFS and RSC Tornado TDN851 AFS are designed for “warm data”. It contains 32 SSD EDSFF E1.L drives up to 61.44 TB each, so it provides up to 1966.08 TB storage in a 1U rack. As new higher-density SSDs appear on the market, the total volume will increase to 2 PB or more in 1U rack.
Cost of Software
The cost of the "RSC BasIS Storage" software is calculated individually. Contact information for inquiries about the software and pricing is provided below.








